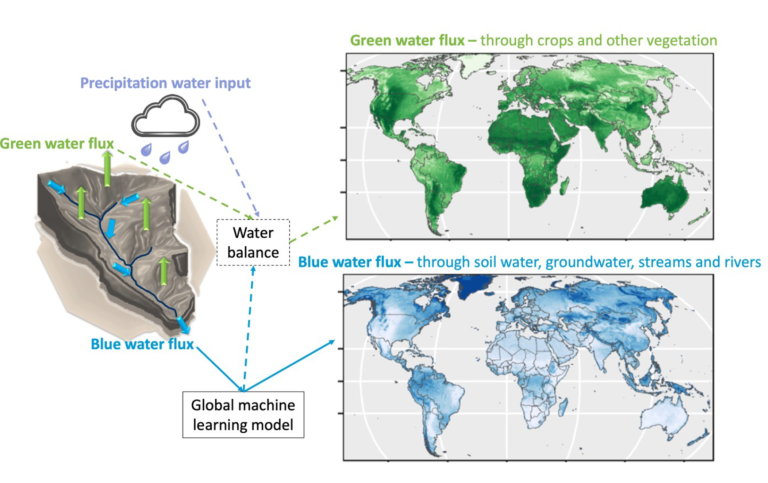
A new study in the scientific journal ‘One Earth’ uses Machine Learning to model and show how the balance of freshwater flows varies across the Earth’s land surface. The results can be used to plan our future land and water use. The balance is particularly vulnerable under current and future climate change, as well as increasing food needs for a growing population.
The paper “Global patterns in water flux partitioning: irrigated and rainfed agriculture drives asymmetrical flux to vegetation over runoff,” by Digital Futures faculty member Gia Destouni and postdoc Daniel Althoff at Stockholm University, has just been published in One Earth.
Water on land is partitioned into a green flux that mainly sustains terrestrial ecosystems and societal food security and a blue flux that mainly sustains aquatic ecosystems and societal water security. The study shows that the green flux is mostly greater than the blue around the world. Expanding crops and irrigation to feed a growing human population will shift more blue water into green, exacerbating the blue water vulnerability to future climate change.
“These results are important to better plan and adapt our land use and balance between different freshwater flows to meet different water needs in society,” says Daniel Althoff from the Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University.
 “The global machine learning model we have developed in the study is a promising tool for predicting the availability of blue and green water under different future climate and land use scenarios around the world,” says Gia Destouni, Professor of Hydrology, Hydrogeology and Water Resources at the Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University.
“The global machine learning model we have developed in the study is a promising tool for predicting the availability of blue and green water under different future climate and land use scenarios around the world,” says Gia Destouni, Professor of Hydrology, Hydrogeology and Water Resources at the Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University.
Gia is also an Affiliated Professor of Engineering Hydrology at KTH Royal Institute of Technology and the Editor-In-Chief of Water Resources Research at the American Geophysical Union.
Althoff D., Destouni G., Global patterns in water flux partitioning: Irrigated and rainfed agriculture drives asymmetrical flux to vegetation over runoff, One Earth, 6(9), 1246-1257, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2023.08.002
Link to Graphical abstract, short description, highlights and Science for Society summary
Find out more in this article at Stockholm University: https://www.su.se/institutionen-for-naturgeografi/nyheter/viktigt-att-vi-lär-oss-balansera-mellan-olika-behov-av-sötvatten-1.674086
Contact:
Daniel Althoff
daniel.althoff@natgeo.su.se
Georgia (Gia) Destouni
georgia.destouni@natgeo.su.se