About the project
Objective
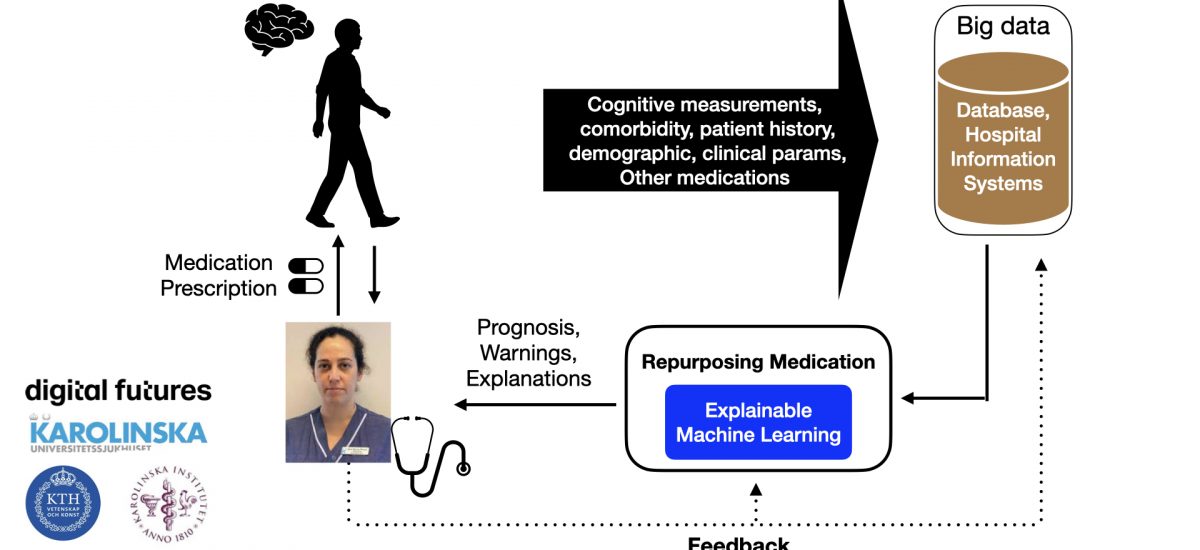
Medical doctors often face difficulty to choose a set of medicines from many options available for a patient. Medication is expected to be disease-specific as well as person-specific. Individual patients may respond differently to the same medication, so the selection of medication should be personalized to everyone’s needs and medical history. In this project, we will explore how AI (artificial intelligence) can help doctors to identify existing medications and/or therapies that can be repurposed for the treatment of dementia.
Dementia is a large-scale health care problem, where around 10% of the population more than 65 years of age suffers from it. Therefore, if AI can assist clinicians in medication selection for dementia patients, it would lead to a significant improvement in the efficiency of treatment. AI can also predict decline (or worsening) of a patient’s health condition over time. Clinicians and healthcare systems will then get precious time to decide life-saving interventions. This heralds use of AI-based medications. The pressing question: can we trust AI systems, mainly its core called machine learning (ML) for patient data analysis and predictions to doctors? Can the ML algorithms explain their predictions to the doctors? In a joint collaboration with Karolinska University Hospital (KUH), Karolinska Institute (KI) and KTH, we will develop trust-worthy ML algorithms with explainable results, and then explore the algorithms to discover new uses for approved medications that were originally developed for different medical conditions.
Background
XML based medication repurposing for dementia (XMLD) refers to the development and application of XML algorithms to identify potential drugs among existing drugs or medications that can be repurposed for the treatment or management of dementia. The goal is to develop XML algorithms to discover new uses for approved drugs or therapies that were originally developed for different medical conditions in patients with dementia. Therefore, for a patient and/or a class of patients, identification of potential drugs among many existing drugs is a variable selection problem, where XML can help.
Therefore, The XML algorithms will be developed to analyze and identify patterns, relationships, and potential associations between drug characteristics, disease severity, and patient outcomes. There are many advantages of medication repurposing for dementia using XML, such as cost and time saving, safety profile, broad range of medication candidates, and improved treatment efficiency. Overall, it addresses a pressing healthcare problem with potentially widespread impact. While our focus is dementia in this project, the accumulated technological knowledge can be used for medication repurposing of many other health problems and diseases in clinics. The proposed XMLD project will establish a strong cooperation between medical doctors and ML researchers in the clinical environment.
Partner Postdoc
Xinqi Bao
Main supervisor
Saikat Chatterjee
Co-supervisor(s)
Martina Scolamiero